Any geological structure/formation/strata which contains water is called as a Water bearing formation. Typically, water bearing formations are named as Aquifers in geology. Those structures have capacity to absorb or transmit water, and generally formed as soil or rock formations.
Most of the aquifers are highly porous and permeable. Thus, those structures are mainly taken as the predominant sources of groundwater applications. Sandstones, Conglomerate, Unconsolidated gravel, Fractured Limestones and fractured volcanic rocks make good aquifers in the nature. These aquifers have a considerable amount of recharge to the ground water storage, because the availability of percentage of pore spaces are higher in the above rock types.

Fig.01: Deference of porosity
According to the occurrences, the aquifers in the underground can be classified in to main four types.
- Unconfined Aquifers
- Confined Aquifers
- Leaky Aquifers
- Perched Aquifers
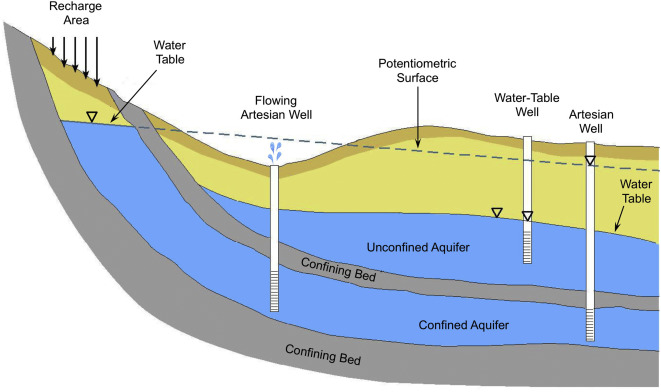
Fig.02: Aquifer types
In order to upsurge the productivity of a well, it should be penetrated into an aquifer. Aquifers have two hydrological properties, such as Storage properties and Transmission properties. Whether, the absence of any of these hydrogeological properties in a certain kind of geological formation can lead to form three different types of hydrogeological unites.
- Aquitards
An aquitard is a geological formation which does not store an appreciable amount of water, but mostly permits water through vertically. However, it does not yield enough as much as aquifer does with its partly permeable nature. Most of the aquitards formed with Silt, Shale, Clay.
- Aquicludes
An aquiclude is a geological feature which stored a considerable amount of water in it and does not transmit water through the formation. This mainly happens with the high porosity of the aquiclude’s medium. Therefore, the aquiclude’s may contain clay, shale.

Fig.03: Aquitard and Aquiclude
- Aquifuge
An aquifuge is an impermeable geological structure which does not store water in it and at the same time, it cannot transmit water through it. The Fresh Crystalline rocks are good example for an aquifuge.

Fig.04: Aquifuge

