H.G. Naduni Erandika*1, B.M.D.B. Basnayake1, M.A.A. Nayanamali2, Rangi Kandane-Rathnayake3, A.W.M. Wazil1, H.P.M.A. Shanthi1, N. Nanayakkara1
1Department of Nephrology, National Hospital-Kandy, Sri Lanka
2Faculty of Nursing, University of Colombo
3Rheumatology Division, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia
Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease activity index (SLEDAI) is utilized to assess the disease progression and to evaluate the clinical improvement following treatment. The study aims to evaluate and compare the disease activity in lupus nephritis (LN) patients on different immunosuppressive drug combination therapies.
Methods: This was a prospective observational study among 82 biopsy proven LN patients attending to Nephrology and Transplant Unit, National Hospital Kandy, Sri Lanka. The follow-up evaluation was performed after six months from the baseline assessment. The SLE disease activity was calculated according to the SLEDAI.
Results: In this patient cohort (N=82), the female-to-male ratio was 8:1with the mean age of 36.2 years (median=35; SD=9.9). The main immunosuppressive medications among the study population were myco-phenolic mofetil (MMF), tacrolimus, azathioprine, and prednisolone. All patients were on prednisolone. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was pre-scribed to 76.8% (N=63) of the patients. There were 6 drug combination groups (Figure 1). The majority of the patients were managed with MMF, Prednisolone and HCQ combination therapy (36.6%; N=30).The highest mean SLEDAI decline during the follow-up period was observed in prednisolone and azathioprine (SLEDAI-2K =3.16) drug combination group (Figure 1). There was a statistically significant difference (p=0.002) between baseline SLEDAI (3.23±4.61) and SLEDAI after six months (1.57±2.52). All the drug combination therapies were effective in improving the SLE disease activity in this study cohort(Figure 1). Moreover, linear regression analysis revealed that, baseline eGFR (=0.976, p=0.000; CI=0.935-1.017) and baseline SLEDAI (=-0.276, p=0.021; CI=-0.510- -0.043) had 96.7% predictable ability (R2=0.967) of the kidney function at the end of 6 month.
Conclusions: All immunosuppressive drug combinations used for the lupus nephritis management was effective as having significant improvement in the SLEDAI after six months of treatment with the highest SLEDAI decline in prednisolone and azathioprine drug combination.
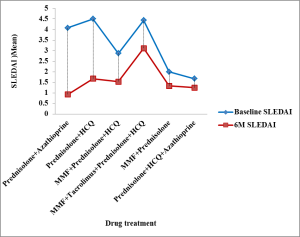
Figure 1: Fluctuation of SLEDAI (SLE disease activity) with medical management
![]()


