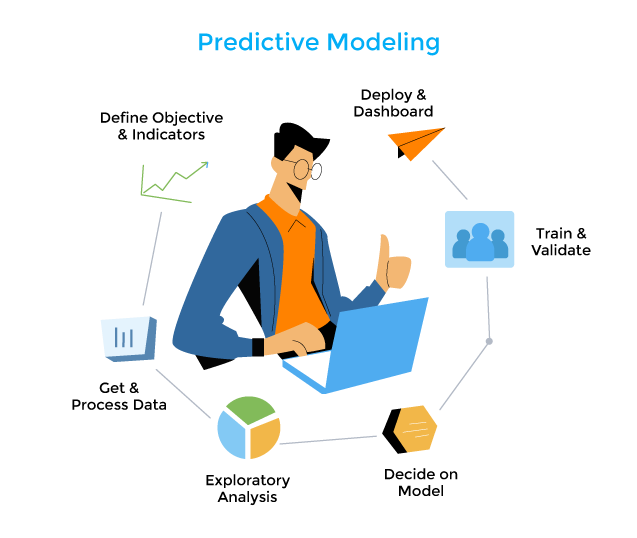
Utilizing predetermined outcomes to develop, process, and validate models is known as predictive modelling. To develop, process, and evaluate a model that can be used to predict future outcomes, predictive modelling is the process of employing known findings. It is an instrument used in predictive analytics, a data mining technique that seeks to provide an answer to the question, “What might occur in the future?” Represents a model that can be applied to make predictions about the future. It is an instrument used in predictive analytics, a data mining technique that seeks to provide an answer to the question, “What might possibly occur in the future?”
To build predictive models that will be utilized to produce an output, predictive analytics leverages predictors or well-known attributes. A predictive model can determine how several data points relate to one another. Regression and neural networks are the most often used predictive modelling methods.
Regression is the statistical term for a linear relationship between the variables used for the input and output. One predictor or feature is needed in a predictive model with a linear function to forecast the output or result. For instance, a bank may use a linear predictive model to identify money laundering in its early phases.
Neural networks, including machine learning and deep learning, which are artificial intelligence (AI) areas, also use predictive models. The neural networks, the cornerstone of artificial intelligence, are built using a web of interconnected nodes in hierarchical levels and are inspired by the human brain. The strength of neural networks resides in their capacity to manage non-linear data interactions. They can establish connections and patterns between variables that human analysts might find difficult or time-consuming to do.

